Description
Learn the various subcategories of cyber security and how they work to guard users and businesses against cyber related risks. Read about network security Concerns, End- User Endpoint Security, Cloud Security, and several others in the ultimate guide.
Introduction
So let me introduce you to cyber security: the protection of data and computer systems in a digital world where it is compulsory. Incidents occur every 39 seconds and cybersecurity helps protect against threats to our information, computer systems, and networks. That however, leads to another question due to the many types of cyber security available out there today. Which is why this guide exists; to provide readers a brief on the main categories of cyber security ranging from network security to cloud security. If you are an IT guy or just concerned reader interested in protection of personal information, this is your ultimate cyber security type guide.
What is Cyber Security?
• Key ideas of cyber security and its role in the world of today.
• Examples of threats connected with the use of computer networks and technologies (virus, phishing, ransomware, etc.).
• Cybersecurity threats on business and individuals.
• Examples of cyber threats (malware, phishing, ransomware, etc.).
• The growing impact of cyberattacks on businesses and individuals.
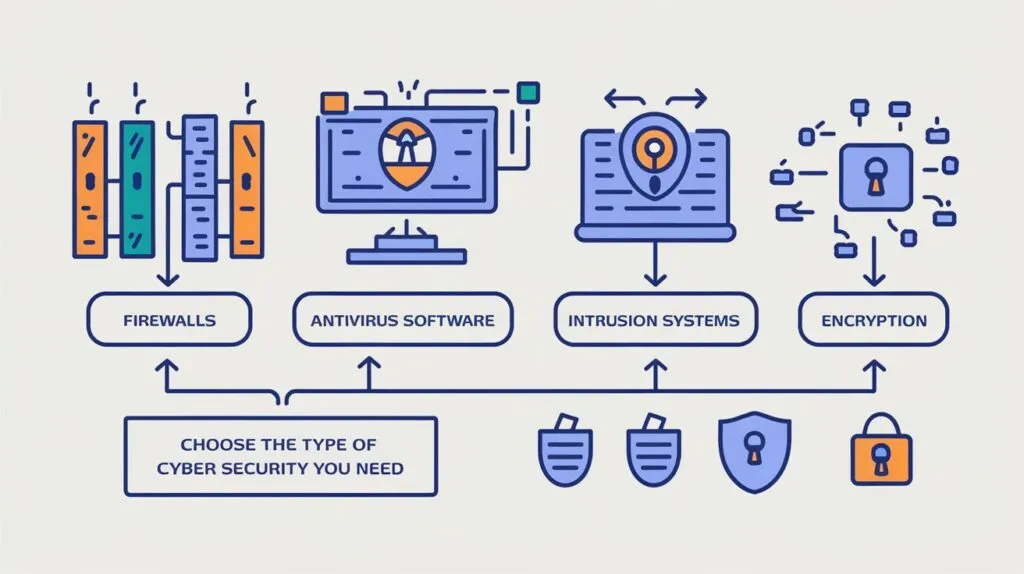
The Importance of Understanding Cyber Security Types
• Ways through which the understanding of the various types of cyber security reduces risks.
• Advantages to various entities including the businesses, government and individual users.
• Best practices and worst practices that were seen in organizations. Benefits for businesses, governments, and personal users.
• Real-world case studies of cyber security successes and failures.
Types of Cyber Security
1. Network Security
• Secure internal and external networks.
• Common tools: firewalls, VPN, interested and detection, Intrusion Detection Systems.
• How to apply network security measures successfully. Mon tools: firewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection systems.
• Best practices for implementing network security.
2. Endpoint Security
• What is endpoint devices? (laptops, smartphones and IoT).
• Avant-garde of Anti-virus applications, and the devices management tools.
• Problems in endpoints’ protection (BYOD, remote access).hones, IoT).
• Role of antivirus software and device management solutions.
• Challenges in endpoint security (BYOD policies, remote work).
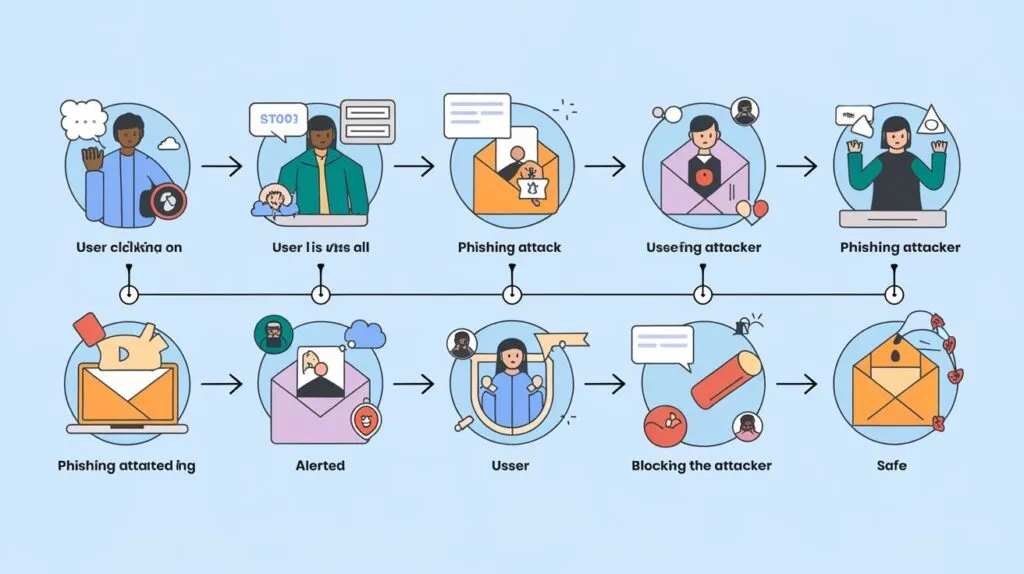
Endpoint Security: Protecting the Devices at the Edge
Endpoint security remains an important part of strong cybersecurity measures and aims at the protection of endpoint gadgets including laptops, desktops, mobiles, tablets, and IoT devices. Cyber attackers prefer getting into the devices mainly because they act as gateways that provide easy access to the targeted online network.
- Endpoints are at risk because they are located away from the central network and might connect to a public Wi-Fi, cloud environments, or even remote working settings. These devices can be threatened by malware attacks, ransomware attacks, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access hacking attacks which would result in leakage of data information, losses of money and tarnishing of organizations reputation.
- To reduce these risks endpoint security utilizes antiviruses tools, endpoint detection and response (EDR), firewalls, and mobile device management (MDM). It offers features like threat monitoring, encryption, and controls over devices so as to give a full coverage as it’s solutions.
- Nevertheless, security for endpoints has its drawbacks. With the adoption of remote work and BYOD, the doors have been thrown wide open to create more avenues where standardization of security cannot be implemented. Also keeping track of updates and patches on a variety of devices and platforms can consume a lot of effort.
- Best practices must be followed to have the most successful endpoint security solution. MFA must be deployed by organizations, strict access rights must be adhered to and, applications should be updated often to close the potential loopholes. Awareness of common phishing tactics, with a reminder for employees on how to respond also enhances organizational security.
- Due to the nature of threats emerging slowly and continuously, the goal of endpoint protection is gradually moving to the modern approach, including zero-trust principles and artificial intelligence-based solutions. These innovations assist organizations in managing emerging risks in their environments and guarantee that end point devices remain secure while allowing users to work in the environment with confidence.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|
| Definition | Endpoint security involves protecting endpoint devices like laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices from threats. |
| Examples of Endpoints | Laptops, desktops, smartphones, tablets, servers, IoT devices, and point-of-sale (POS) systems. |
| Common Threats | Malware, ransomware, phishing, unauthorized access, and device loss or theft. |
| Key Tools | Antivirus software, firewalls, endpoint detection and response (EDR), mobile device management (MDM). |
| Techniques | – Device encryption – Application control – Sandboxing – Real-time threat monitoring |
| Challenges | – Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies – Remote work setups – Keeping software updated across all endpoints |
| Best Practices | – Enforce strong passwords and MFA – Use encryption for sensitive data – Regularly update software and firmware |
| Emerging Trends | – Zero-trust architecture – AI-driven threat detection – Integrated EDR and XDR solutions |
| Real-world Examples | – Preventing ransomware attacks on healthcare devices – Securing remote worker laptops during the pandemic |
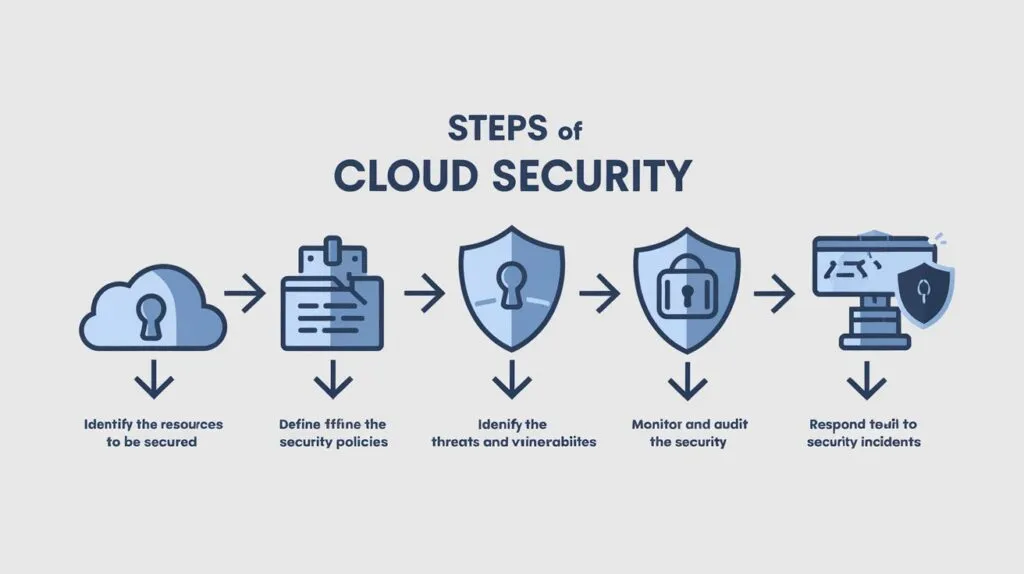
3. Cloud Security
- Safeguarding data stored in cloud environments.
- Key solutions: encryption, identity management, and secure APIs.
- Emerging threats in cloud computing (misconfigurations, insider threats).
| Aspect | Details |
| Definition | Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and services stored or operated in cloud environments. |
| Key Threats | Data breaches, misconfigurations, insider threats, DDoS attacks, and insecure APIs. |
| Primary Goals | – Ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability – Protect against unauthorized access – Maintain compliance with regulations |
| Core Components | – Data Protection: Encryption and backup – Identity Management: MFA, IAM – Monitoring: Real-time threat detection |
| Security Tools | – Secure Web Gateways (SWG) – Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) – Encryption solutions – Threat intelligence platforms |
| Challenges | – The complexity of the multiple cloud environments The nature of European cloud services means that the roles are partially divided between the cloud providers and the users. This resulted from human error and misconfigurations of the systems that the JD Edwards application was launched to streamline. |
| Best Practices | – Use strong encryption for data in transit and at rest – Implement zero-trust policies – Regularly audit and monitor cloud infrastructure |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhere to regulations like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and SOC 2 for secure cloud usage. |
| Emerging Trends | – AI-based security automation – Secure DevOps practices (DevSecOps) – Increased use of SASE frameworks |
| Real-world Examples | – Protecting customer data in SaaS applications – Preventing unauthorized access in cloud storage platforms |
4. Application Security
- Protecting software applications from vulnerabilities.
- Security measures: code reviews, penetration testing, and updates.
- Examples of application security breaches and their consequences.
Application Security: Protecting Software Delivery in the New Millennium
- Application security is also sub-pillar of cyber security: this involves the protection of applications used within an organization from six key vulnerabilities. With technology rapidly developing and organization using application for their business processes, it is apparent that securing these tools is critical.
- Application security refers to that set of measures that is incorporated in application development, deployment and management phases in order to protect an application. The threats include attack on applications’ flaws with open doors such as SQL injection, cross site scripting (XSS), and insecure deserialization that may call for loss of data, revenue or goodwill.
- Some of the most critical tools for application security include and application security testing which comprises SAST and DAST and other real-time technologies such as WAF and RASP. They detect weaknesses that may potentially be exploited, while precluding harm from being done.
- Secure Development Lifecycle (SDLC) is applied to incorporate factors of security into the development process from design to deployment. More specifically, now penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are conducted more regularly to make sure the application remains immune to new threats.
- Many of the problems associated with application security are found in the DevOps and agile development environments, where development cycles are short. Security and convenience; Third party libraries; Complex coded structures; Need monitoring, developers with security team.
- New approaches like DevSecOps, bring security from a separate entity into integrated process of software development. Artificial Intelligence is expanding its capabilities to detect threats, whereas microservices and API protection are emerging in modern designs.
- Today, applications interface with the functionality of both personal and business processes and therefore security is paramount. Through integrated extensive security measures and always getting update with new security threats, organizations can defend their applications and the users’ confidence within the connected cyber realm.
| Aspect | Details |
| Definition | Application security involves protecting software applications from vulnerabilities and external threats during development and deployment. |
| Key Threats | SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure deserialization, broken authentication, and misconfigurations. |
| Primary Goals | – Ensure application confidentiality, integrity, and availability – Protect user data from unauthorized access – Prevent exploitation of vulnerabilities |
| Core Components | – Code Security: Secure coding practices, static and dynamic code analysis – Access Control: Authentication, authorization, and session management – Testing: Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning |
| Security Tools | – Web Application Firewalls (WAF) – Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools – Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools – Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) |
| Challenges | – Identifying vulnerabilities in complex applications – Balancing security with functionality – Addressing security in agile and DevOps workflows |
| Best Practices | – Conduct regular security assessments and code reviews – Implement secure development lifecycle (SDLC) processes – Keep third-party libraries and frameworks updated |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensure compliance with GDPR, OWASP Top 10, PCI DSS, and other relevant standards. |
| Emerging Trends | – DevSecOps integration for security in CI/CD pipelines – AI-assisted threat detection in applications – Microservices and API security |
| Real-world Examples | – Preventing data leaks in web applications – Securing APIs in fintech and e-commerce applications |
5. Data Security
- Ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
- Techniques: encryption, backup, and access controls.
- Legal implications of data breaches (GDPR, CCPA).
What is Data Security?
Information security, or data protection as it is often called, encompasses techniques and processes used to protect information from inadvertent or deliberate loss, alteration or theft at any time in its existence. They guarantee that such information do not leak to the wrong hands, is not interfered with in anyway, and is available for use by those permitted to access it. Flaxman also notes that with most transactions, cloud computing or interconnected systems, protection of data is paramount for anyone from an individual to business to government.
Key Threats to Data Security
Today’s data security threats can be categorized into; Data breaches, ransomware attacks, insider threats, and malware. Another significant risk is non-malicious one, resulting from human actions for example, deleting files, misconfigurations intentionally or unintentionally. In light of hybrid and multi-cloud usage it became even easier for organizations to lose track of sensitive data and protect it across various platforms.
The parameters essential to data security have been described in the following points:
Encryption:
Assures that data is comprehensible only to the entitled users while in transit and in stored status.
Access Control:
Provides means of controlling review access using role-based permissions and also ensures that user grants multiple factors of authentication when permitting data access.
Backup and Recovery:
There is always a duplicate to obtain information in case of deluge or hacking.
Industry’s leading practices relevant to data protection
The needs for better security for the information should be addressed by classifying the data, protecting the most sensitive data first and performing periodic assessments of the data for access and activity. A form of vulnerability is covering up basic software and hardware patches by continuously updating them.
Why Data Security Matters
Do not consider data security a topic confined to laws such as GDPR or HIPAA; data security is the foundation for customer trust and business resilience against financial and reputational losses. Data security measures remain the key to a secure organization especially given that modern operations occur in cyberspace.
Measures that are used in the protection of data make sure that there is conformance but also make sure that organizations are sustainable in the current society that is driven by technology.
| Aspect | Details |
| Definition | Data security involves protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft throughout its lifecycle. |
| Key Threats | Data breaches, ransomware, insider threats, accidental deletions, and malware attacks. |
| Primary Goals | – Ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad) – Secure persons’ right violations and leakage of important information – Comply to the legal and regulatory requirement |
| Core Components | – Encryption: Protecting data in transit and at rest – Access Control: Role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication (MFA) – Backup and Recovery: Ensuring data redundancy and disaster recovery |
| Security Tools | – Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions – Encryption software – Secure file transfer protocols – Data classification and monitoring tools |
| Challenges | – Protecting data in hybrid and multi-cloud environments – Identifying sensitive data across large datasets – Addressing human error in data handling |
| Best Practices | – Classify and prioritize sensitive data – Regularly audit access permissions – Use strong encryption standards (e.g., AES-256) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Comply with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX for secure data handling. |
| Emerging Trends | – Data classification made easier by AI, as well as the analysis of anomalous patterns. important techniques such as Homomorphic encryption – Blockchain as a measure of security and control in data management |
| Real-world Examples | – Encrypting financial data for e-commerce platforms – Using DLP to prevent sensitive data leakage in healthcare organizations |
Conclusion
Cyber security is a broad discipline and genre that has many interrelated sub genres, all of which are crucial for countering particular kinds of threats. If you know what each type entails, you can ensure that your defense mechanism is very strong regardless of the challenge that comes your way. This means that as the development of technology increases as well the most effective way to protect yourself from the cyber attack will be to be informative and prepared. Start now – assess your existing security environment and discover new ways to protect your digital tomorrow!


