Description:
Read our article on the key trends and concepts for mobile security in the year 2025. Get to know how to protect your information, and avoid becoming a victim of a cyber attack.
Introduction:
You will be surprised to learn of recent statistics that reveals that mobile devices contribute more than 70% of internet traffic. This rise has brought into the spotlight the aspect of mobile security as has never happened before. In devices, from individual gadgets to business networks, the dangers of mobile threats are continually increasing. Smartphone, tablet, and IoT are the most common entry points where cyber criminals seek to take advantage of holes into getting data. But want to make you feel better – with this guide you will arm yourself with the knowledge that will help you protect your mobile devices in 2025 and further.
1.What is Mobile Security and Why Does It Matter?
- Definition and importance of mobile security
- Rising threats targeting mobile devices (e.g., malware, phishing, ransomware)
- Impact of mobile security breaches on individuals and businesses

2.Common Mobile Security Threats in 2025
- Mobile Malware:
- How it spreads and the damage it causes
- Notable recent attacks on mobile platforms
- Phishing Scams:
- Examples of SMS phishing (smishing) and email phishing
- Ways to identify and avoid phishing attempts
- Unauthorized Access:
- Risks of lost or stolen devices
- Importance of device encryption and secure authentication
3.Best Practices for Mobile Security
- Strengthen Device Security:
- Use strong passcodes and biometric authentication
- Enable remote lock and wipe features
- Update Regularly:
- Importance of keeping apps and operating systems updated
- Automatic updates vs. manual updates
- Be Cautious with Apps:
- Risks of downloading apps from unverified sources
- Permissions management and privacy considerations

4.Mobile Security for Businesses
- Implementing Mobile Device Management (MDM):
- Overview of MDM solutions and their benefits
- Enforcing security policies across employee devices
- Securing BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Policies:
- Challenges and solutions for employee-owned devices
- Data segregation and secure access protocols
- Educating Employees:
- Training on mobile security best practices
- Regular updates on emerging threats
5.Emerging Trends in Mobile Security
- 5G and Its Security Implications:
- Opportunities and risks with faster connectivity
- Solutions to mitigate 5G-related vulnerabilities
- AI and Machine Learning in Mobile Security:
- Role of AI in detecting and preventing threats
- Limitations and challenges of AI-driven security
- Blockchain for Mobile Security:
- Applications of blockchain in secure communications
- Benefits for mobile payment systems and data privacy
6.Tools and Apps for Enhancing Mobile Security
- Top Mobile Security Apps in 2025:
- Features to look for (e.g., antivirus, VPNs, firewalls)
- Recommendations for Android and iOS platforms
- Network Security Tools:
- Importance of secure Wi-Fi connections
- Benefits of using VPNs for public network safety
7.The Future of Mobile Security
- Predictions for mobile security advancements in the next decade
- How businesses and individuals can prepare for evolving threats
Conclusion:
Security in mobile is not any more an option, but a paramount need in an interlinked world. When you know how hackers attack, act according to the recommendations of specialists, and use special software you can guard your devices and information against cybercriminals. In 2025, being keen and active is important whether as an individual, company or an organization. Don’t wait for tomorrow and get ready for your mobile tomorrow today.

2.Understanding Operational Security (OPSEC): One of the most important elements of risk management
OPSEC or Operational Security is a fundamental procedure needed to safeguard classified information and organization processes. OPSEC was first designed for war purposes and has later spread to business organizations, government and even individual use to protect sensitive information from the enemies.
What is Operational Security?
OPSEC is a deliberate process to pinpoint the source and weakness with business data together with the levels of risk and protective steps to cease intelligence gathering by hostile individuals. It focuses on showing how even the most innocuous of data can be exploited by a competitor in a jigsaw and used against a business.
The Five Steps of OPSEC
1. Identify Critical Information: Identify which of the organization’s data is sensitive and should therefore be protected or is sensitive in nature and should be safeguarded e.g., trade secrets, financial records, or business strategies.
2. Analyze Threats: Find out who the threat could be: an outsider hacker, the competition, or an insider and what they are capable of.
3. Assess Vulnerabilities: Identify points of vulnerability pertaining information: {Review processes/programs AND people}.
4. Implement Countermeasures: They also need to implement safety measures such as encryption, secure connection, or employee awareness as concepts.
5. Monitor and Evaluate: Prolonged operation should be check for emergent threats while the performance of put measures should also be assessed.
Why is OPSEC Important?
Technology is advancing today and so is the piracy and theft of personal data an corporations’ digital information. An effective OPSEC plan means that organisations should be in a position to reduce risks or vulnerabilities, safeguard critical and sensitive assets as well as ensure confidence of their stakeholders.
Conclusion
Operational Security is not simply a technique – it is an attitude. Identifying and managing risks is a key to warding off threats that compromise the performance of individuals and companies that work in the digital world of today, where threats are becoming more and more diversified.
3.Internet of Things (IoT) Security: Protecting a Connected World
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how we interact with technology, enabling billions of devices to communicate seamlessly. From smart homes and wearable devices to industrial systems, IoT has made our lives more efficient and interconnected. However, this connectivity also brings significant security challenges.
What is IoT Security?
Internet Of Things is abbreviated as IoT security which defines the security standard that exist in IoT gadgets or connections to minimize cyber hazards.. Given the vast number of connected devices—projected to exceed 30 billion by 2025—ensuring robust security is critical to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining system integrity.
Common IoT Security Challenges
- Weak Authentication: Many IoT devices lack strong passwords or rely on default credentials, making them easy targets for attackers.
- Data Privacy Risks: IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal and sensitive data, which can be exposed in a breach.
- Lack of Standardization: The absence of unified security standards leaves many devices vulnerable.
- Botnet Threats: Infected IoT devices can be hijacked and used in massive botnet attacks, such as the infamous Mirai botnet.
Best Practices for IoT Security
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices.
- Regularly update device firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
- Enable encryption to secure data transmission.
- Segment IoT devices on separate networks to limit exposure.
- Monitor network activity for unusual behavior.
Conclusion
IoT security is essential to ensuring a safe and reliable connected environment. As IoT adoption continues to grow, individuals and organizations must prioritize robust security measures to mitigate risks and protect their digital ecosystems. A proactive approach to IoT security safeguards the benefits of this transformative technology while minimizing potential threats.
4.Identity and Access Management (IAM): Securing Digital Access
IAM is critical in today’s interconnected world as it ensures that an organization protects its information while at the same time allowing the right person access the right information or resource. IAM solutions are indispensable for managing and checking user identities in a rapidly developing threat environment.
What is IAM?
IAM consists of policy, tools and other functions which are used for maintaining and controlling users’ accounts as well as access to systems, networks and data. There is a practice of personnel management that organizes employees’ access in such a way that prevents emergent threats from insiders.
Key Components of IAM
1.Authentication:
Authenticate users, using password, physical characteristics such as fingerprints, or MFA among other techniques.
2.Authorization:
Assigning rights to the user depending on his position, permissions and policy.
3.User Lifecycle Management:
Controlling the process of creating, maintaining, and retiring identities of individuals that enter, change, or exit an organizational context.
4.Access Governance:
The use of logs for monitoring and auditing access rights to execute control and implement laws and policies.
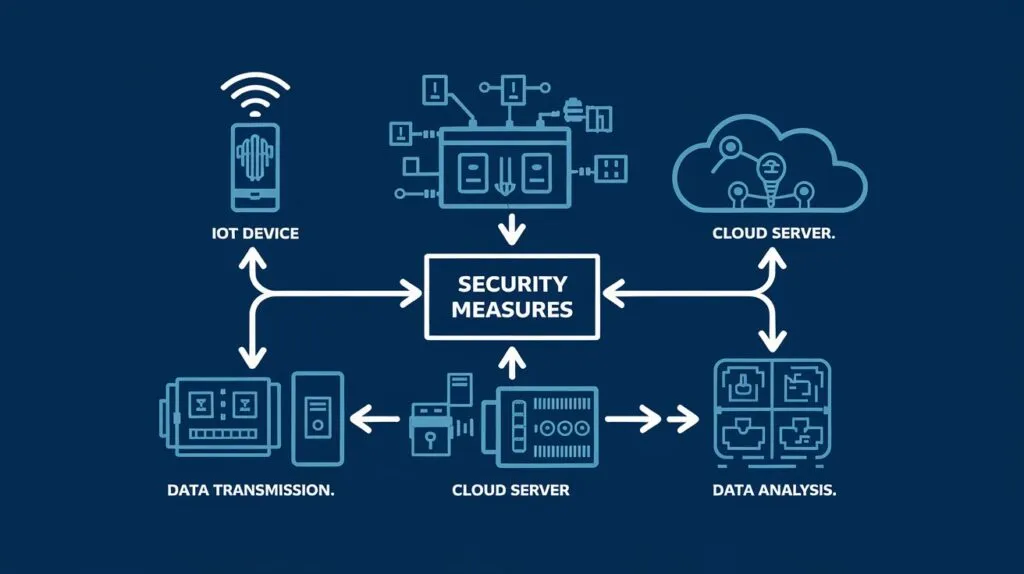
Benefits of IAM
• Enhanced Security: Contains private information through restricting its access to only those who need it.
• Improved Efficiency: Enables the automation of user access processes consequently minimizing work load and blunders.
• Regulatory Compliance: Serving the purpose to help organizations to fulfill their obligations of the GDPR, HIPAA, and other such regulations.
Conclusion
Identity and Access Management is one of the foundational elements in the discourse on contemporary cybersecurity. It is therefore important for organizations to put in place strong IAM solutions to enhance network security, efficiency and customers/ stakeholders confidence. As the threats in cyberspace space become more diverse, IAM becomes crucial to providing a safe and sustainable environment.
5.Critical Infrastructure Security: Protecting Vital Systems
Critical infrastructure signifies the core components and commodities of socioeconomic existence, which can be termed as critical infrastructure – electricity, water supply. Chain networks, transportation systems, Communication networks. Protecting such structures is central because their threat is immense relative to national security, public health, and the economy.
First of all, let us attempt at defining what Critical Infrastructure Security is.
Critical Infrastructure Security is the protection of physical and information technologies from various risks such as hackers attack, disasters, and mistakes. Albeit being an important task, safeguarding these structures is challenging due to how systems’ integration has been enhanced through digitization.
Main Risks in Relation to ASP Federation
1. Cyberattacks:
Advanced malware, ransomwares, and state actors exploit the flaws in the important infrastructures.
2.Insider Threats:
Employees through intentional or unintentional mistakes may act in ways that pose a risk to system security.
3.Physical Attacks:
A sabotage or a terrorism in certain elements like power plant or pipelines.
4.Natural Disasters:
Business continuity can also be disrupted by acts of terrorism, natural disasters such as earthquake, floods as well as hurricanes.
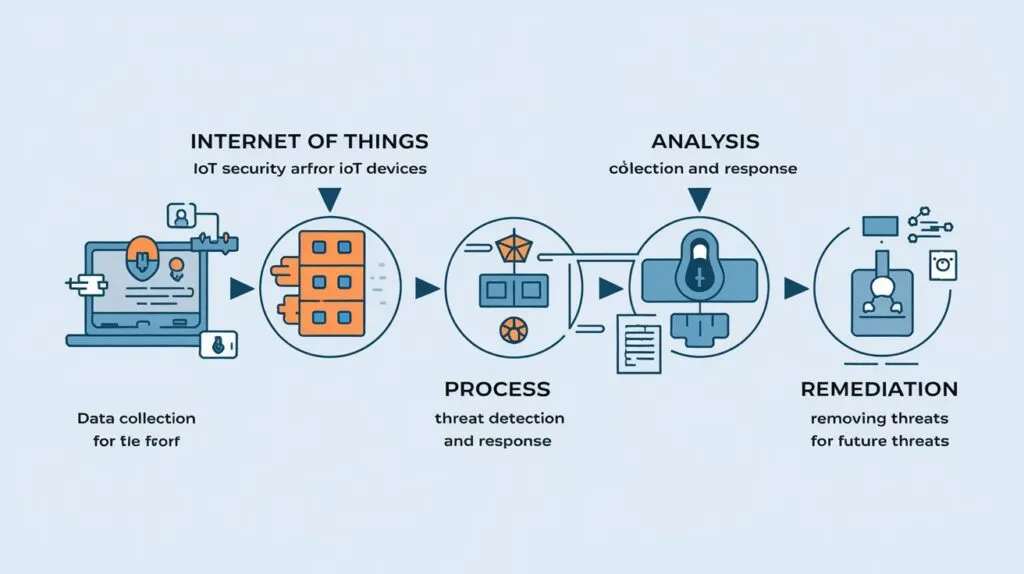
Risk Management Planning for Critical Infrastructure
• Implement Cybersecurity Frameworks: Stakeholder management is inform of adopting better standards such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework for risk assessment.
• Enhance Monitoring and Detection: Integrate high sophisticated threat detection systems through which the incident can be detected and a reply initiated immediately.
• Strengthen Access Controls: Use IAM to have restricted system access to only relevant personnel.
• Promote Public-Private Collaboration: Stimulate government and private players by offering incentives that would allow them to combine efforts in threat intelligence sharing.
• Regularly Test Resilience: Functional exercises in order to anticipate and practice how to respond to threats and disturbances.
Conclusion
Sheltering of crucial assets is important to national security and the welfare of citizens. Thus, the general protection measures in coordination with representatives of various sectors and industries will help to consider potential threats and to develop effective protection against them for these systems, which are the basis of many sectors’ performance.


